Using Veeam with XFS (Linux repositories) and ReFS (Windows repositories) combined with Veeam’s Fast Cloning technology provides significant performance and storage advantages, particularly for backup and recovery efficiency. So firstly, let me explain the differences between Block Cloning and Fast Clone technology.
Fast Clone is the Veeam technology that uses the underlying Block Cloning capabilities of a file system like ReFS/XFS to create new backup points without copying data blocks. Block cloning is the file system’s low-level functionality that makes Fast Clone possible by creating new file entries that point to the same data blocks, copying the data only when it’s modified. In essence, block cloning is the “how” at the file system level, and Fast Clone is the Veeam-implemented “what” for creating efficient backups.
| Feature | Description |
| Block Cloning | The low-level function of a file system (like ReFS or XFS) that creates new files by copying metadata instead of data blocks. This allows multiple files to share the same data blocks initially. |
| Fast Clone | The Veeam feature that leverages block cloning to speed up operations like creating synthetic full backups. It makes these operations nearly instantaneous by creating new backup chain points through metadata updates rather than data copies. |
| How they work together | Veeam’s Fast Clone technology is built on top of a file system’s block cloning capability. When Veeam needs to create a new backup file or a synthetic full backup, it instructs the underlying file system to use its block cloning function. |
| Key benefits | Both technologies result in significantly faster backup creation and transformation, reduced storage space, and lower I/O load on the storage device compared to traditional file copying methods on systems like NTFS. |
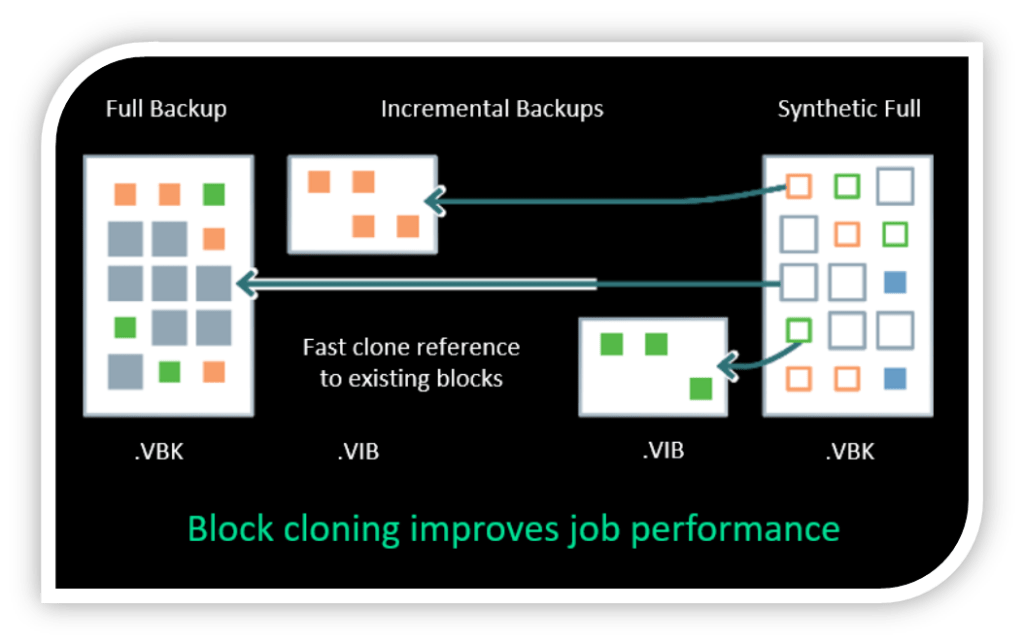
Now let’s get into some key advantages of using this technology:
1. Fast Synthetic Full Backups
Fast cloning enables Veeam to create synthetic full backups without rehydrating and copying entire files. With this technology, Veeam Backup & Replication references existing data blocks on volumes instead of copying data blocks between files. Data blocks are copied only when files are modified.
- Dramatically reduces I/O load
- Synthetic fulls are generated up to 10× faster
- Lower CPU and disk utilisation
2. Massive Space Savings
Because ReFS and XFS simply clone metadata pointers rather than duplicate data:
- Synthetic Full backups use minimal additional storage
- Enables efficient Synthetic forever-forward incremental backup strategies
- Faster and space efficient GFS restore point creation in both backup and backup copy jobs
- Ideal for large environments with long retention policies
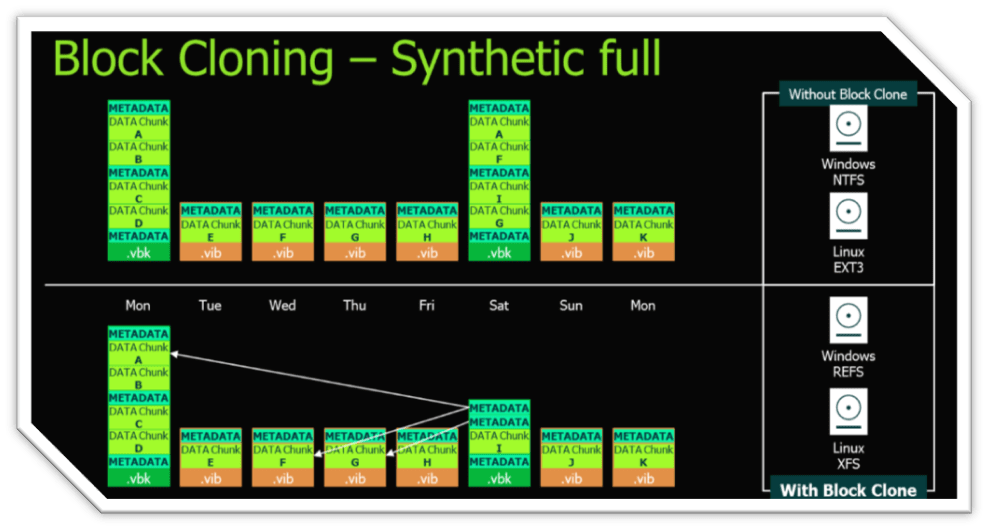
The above graphics compares what a backup looks like in a NTFS/EXT3 formatted filesystem compared to a ReFS/XFS formatted filesystem. Storage savings can be significant.
3. Enhanced Backup Performance
- Improved write speeds during backup and transform operations
- Reduced backup window timeframes
- Less impact on production or repository storage
4. File System Level Optimisation
| Feature | ReFS (Windows) | XFS (Linux) |
| Block cloning | ✔ | ✔ |
| Fast cloning | ✔ | ✔ |
| Preferred for Veeam Appliance | – | ✔ |
| Per-VM backup chain | ✔ | ✔ |
| Reduced storage space | ✔ | ✔ |
| Veeam integration maturity | High | Very high (favoured in v12/v13) |
5. Reliability & Resilience
- ReFS provides built-in data integrity streams and self-healing (with storage spaces)
- XFS offers robust metadata handling and performance tuning
- Both reduce risk of corrupted backup chains
- Lower stress on storage hardware
- Faster restore point creation
When to Use What
- 🟩 Linux + XFS → Recommended default for Veeam v12+ and appliance builds
- 🟦 Windows + ReFS → Still valid for Windows-based repositories
Veeam Backup & Replication supports Fast Clone for the following types of backup repositories:
- Linux server
- Microsoft Windows server
- SMB share
- Dell Data Domain
- ExaGrid
- Fujitsu ETERNUS CS800
- HPE StoreOnce
- Infinidat InfiniGuard
- Quantum DXi
I still come across partners and customers who haven’t yet transitioned to using either ReFS or XFS for there backups. If you would like to move your backups to a ReFS/XFS repository, this can be easily achieved.
To move your backups to another repository and target the backup job to the new ReFS/XFS repository, do the following:
- Create a ReFS/XFS repository under Backup Infrastructure
- In the Home screen, select the Backups node
- In the working area to the right-hand side, right-click a job and select Move backup or select Move Backup from the top ribbon pane.
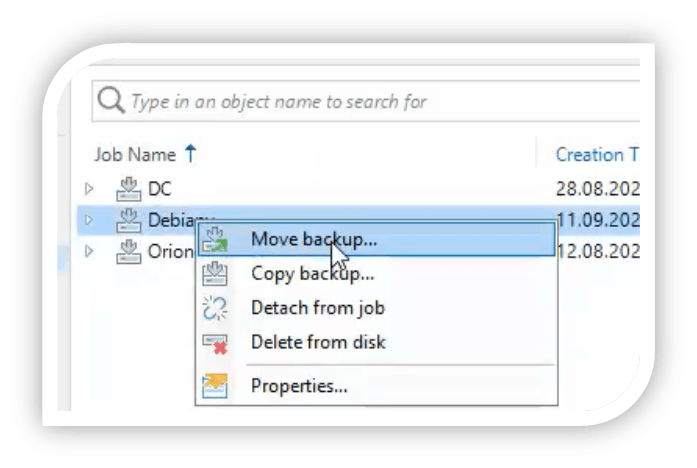
- The Move Backup to Another Location window appears. Here you can select the ReFS/XFS repository you have created. Veeam will reconfigure the backup job to now point to the newly selected ReFS/XFS repository.
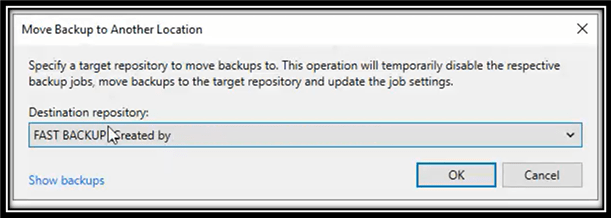
- Click OK and move of repositories starts.
There are some considerations and limitations to consider when moving to a ReFS/XFS repository. Please visit the Veeam KB article on ReFS – https://www.veeam.com/kb2792
Fast Cloning with XFS or ReFS allows Veeam to create full backups instantly by referencing unchanged blocks, drastically improving speed, saving storage, and maintaining efficiency over long retention periods, making it one of the most powerful optimisations for modern backup repositories.
Published: November 27, 2025 5:47pm
Leave a comment